WebKit Features in Safari 18.0
Safari 18.0 is here. Along with iOS 18, iPadOS 18, macOS Sequoia and visionOS 2, today is the day another 53 web platform features, as well as 25 deprecations and 209 resolved issues land in WebKit, the rendering engine driving Safari.
New in Safari 18
Distraction Control
Distraction Control lets you hide distracting items as you browse the web, such as sign-in banners, cookie preference popups, newsletter signup overlays, and more, in Safari for iOS 18, iPadOS 18 and macOS Sequoia.
Activate Distraction Control by tapping the Page Menu 
Viewer
Whenever you are on a web page with a prominent video element, you can click on “Video Viewer” in the Page Menu 
We always recommend using semantic HTML when creating a website, including <video>,<main>, <article> and other elements that describe content. Doing so helps ensure both Safari Reader and Safari Viewer work best for the users of your website.
iPhone Mirroring and remote inspection
With iPhone Mirroring on macOS Sequoia, you can use your iPhone from your Mac. Combine it with remote inspection from Safari, and now it’s easier than ever to test and debug websites on iOS using Web Inspector.
Get set up for remote inspection by first ensuring you have Safari’s developer tools enabled on your Mac (if you can see the Develop menu in Safari, you’ve already done this step). Next, enable Web Inspector on your iPhone at Settings > Apps > Safari > Advanced > Web Inspector. Then, you’ll need to connect the device to your Mac using a cable to grant permission. Once plugged in, your device will appear in the Develop menu in Safari. Finally, to enable wireless debugging, go to Safari on macOS > Develop > [your device] > Connect via Network.
Now you can use Web Inspector to wirelessly debug websites running on iPhone anytime. And with iPhone Mirroring, you don’t even have to pull out your phone. Everything is on your Mac’s screen.
Learn more about remote inspection by reading Inspecting iOS and iPadOS, or by watching Rediscover Safari developer features from WWDC. Learn more about iPhone Mirroring1 on apple.com.
Web apps for Mac
Last year, we added support for web apps in macOS Sonoma. You can add any website to your dock — whether or not it was built with a Manifest file, Service Worker, or other technology to customize the web app experience. Go to the site in Safari, then File > Add to Dock… where you can customize the icon, change the name, and even adjust the URL. Then, just click on the web app icon in your Dock, and the website will open as a stand-alone app.
This year brings two improvements to web apps on Mac.
Opening links
macOS Sequoia adds support for opening links directly in web apps. Now, when a user clicks a link, if it matches the scope of a web app, that link will open in the web app instead of their default web browser. For example, imagine you have added MDN Web Docs to your Dock. Then a colleague sends you a link to an MDN page in Messages, Mail, Slack, Discord, IRC, or any non-browser application on your Mac. Now when you click on that link, it will open in the MDN Web Docs web app instead of your default browser.
Clicking a link within a browser will maintain the current behavior. This feature only affects links opened elsewhere. (When a user is in Safari, clicking on a link that matches the scope of a web app that is added to Dock, they will see an “Open in web app” banner, unless they have previously dismissed the banner.)
By default, this behavior applies when the link matches the host of the web page used to create the web app. As a developer, you can refine this experience by defining the range of URLs that should open in the web app with the scope member in the web app manifest.
Extension support
Now users can personalize web apps on Mac with Safari Web Extensions and Content Blockers. Navigate to the web app’s Settings menu to access all the installed Content Blockers and Web Extensions. Any enabled in Safari will be on by default in the web app. Each web app is uniquely customizable, just like Safari profiles.
CSS
View Transitions
WebKit added support for the View Transitions API in Safari 18. It provides an optimized browser API to animate elements from one state to another. Safari supports the CSS View Transitions Module Level 1 specification that adds new CSS properties and pseudo-elements for defining transition animations, along with a new browser API to start transition animations and react to different transition states. It works by capturing the current (old) state of the page and applying an animated transition to the new state. By default, the browser applies a cross-fade between the states.
Call the document.startViewTransition() method to initiate the capture. You can pass a callback function as the first argument to make DOM state changes between the old and new captures. The method returns a ViewTransition object which contains promises that can be used to track when the view transition starts or ends.
Once the states are captured, a pseudo-element tree is built which can be targeted with CSS, allowing you to modify the CSS animations used for the transitions. The animations out of the old page state and into the new page state can be modified via the ::view-transition-new(*) and ::view-transition-old(*) selectors. You can also ask the browser to independently track state changes for a specific element by naming it with the CSS view-transition-name property. You can then use the pseudo-elements to customize animations for it.
.page-view {
view-transition-name: page-view;
}
::view-transition-old(page-view) {
animation: 500ms ease-in-out transition-out-animation;
}
::view-transition-new(page-view) {
animation: 500ms ease-in-out transition-in-animation;
}
The :active-view-transition pseudo-class becomes active on the root element when a view transition is running.
The example below demonstrates state management with tabbed navigation. Each tab view has a custom transition animation out and a subtly different animation in, while the tabs themselves rely on the default page transition.
Style Queries
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for Style Queries when testing CSS Custom Properties. Similar to how developers can use Sass mixins, Style Queries can be used to define a set of reusable styles that get applied as a group.
Here, if the --background custom property is set to black, then certain styles will be applied — in this case to make the headline and paragraph text color white.
@container style(--background: black) {
h2, h3, p {
color: white;
}
}
Don’t forget to pay attention the HTML structure. By default, Style Queries reference the styles on the direct parent element. You can create a different reference through the use of Container Query names.
currentcolor and system color keywords in Relative Color Syntax
Support for Relative Color Syntax shipped in Safari 16.4. It lets you define colors in a more dynamic fashion, creating a new color from an existing color. The value lch(from var(--color) calc(L / 2) C H) for instance uses the lch color space to take the variable --color and calculate a new color that’s half its lightness, calc(L / 2).
Now in Safari 18.0, the first browser to ship support, you can reference the currentcolor or a system color keyword as you define the new color. For example, this code will set the background color to be the same color as the text color, only 4 times lighter, as calculated in the oklch color space.
section { background: oklch(from currentcolor calc(L * 4) C H); }
Being able to reference system color keywords opens up another world of options. System colors are like variables that represent the default colors established by the OS, browser, or user — defaults that change depending on whether the system is set to light mode, dark mode, high contrast mode, etc. For example, canvas represents the current default background color of the HTML page, while fieldtext matches the color of text inside form fields. Find the full list of system colors in CSS Color level 4.
Relative Color Syntax lets you define dynamic connections between colors in your CSS, lessening the need to control color through variables in a tightly-regimented design system. Learn more about Relative Color Syntax by watching this portion of What’s new in CSS from WWDC23.
Translucent accent colors
Partially transparent colors in accent-color are now blended on top of the Canvas system color to match the latest updates to the web standard. This means that any of the many ways to define colors using an alpha channel will now work as expected when used to define an accent color for a form control.
.form-control {
accent-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.6);
}
Animating display
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for transition animation of the display property.
Many developers are excited to use @starting-style along with transition-behavior and display: none interpolation. WebKit for Safari 17.4 added general support for transition-behavior, including transition-behavior: allow-discrete. WebKit for Safari 17.5 added support for @starting-style, letting you define starting values for transitioning an element as it’s created (or re-created). Now in WebKit for Safari 18.0, you can use these features together to transition the display property.
Backdrop Filter
Originally shipped in Safari 9.0, backdrop filter provides a way to apply graphics effects to the content behind a particular element. You can apply backdrop-filter to a headline, for example, and everything behind the headline will be blurred, or have decreased saturation, or increased contrast. Any of the filter functions from SVG can be used — blur(), brightness(), contrast(), drop-shadow(), grayscale(), hue-rotate(), invert(), opacity(), saturate(), and sepia().
For many years, backdrop filter only worked in Safari. It was available when you prefixed the property with -webkit-backdrop-filter. Now, starting in Safari 18.0, you don’t need the prefix. We also improved our implementation, fixing bugs and boosting interoperability.
This demo shows eight different filters and what you might do with each one alone. You can, of course, combine filters to create even more interesting results. With backdrop filter supported in Safari since 2015, Edge since 2018, Chrome since 2019, Samsung Internet since 2020, and Firefox since 2022, this is a great time to consider the kind of graphic design possibilities it enables.
Content visibility
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for content-visibility. This property controls whether or not an element renders its contents in a fashion that’s useful for making performance optimizations. It lets you communicate to the browser that certain portions of the page will likely be initially offscreen, and suggest they be omitted from layout and rendering. This can make the page load faster.
And more
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds parsing support for the custom value for theprefers-contrast media query. (It does not return “true” on Apple platforms, since there is no forced-colors mode in iOS, iPadOS, macOS or visionOS.)
Spatial Web
WebXR
Safari 18.0 for visionOS 2 adds support for immersive-vr sessions with WebXR. Now you can create fully immersive experiences for people using Apple Vision Pro and deliver them through the web. WebXR scenes are displayed using hardware-accelerated graphics driven by WebGL.
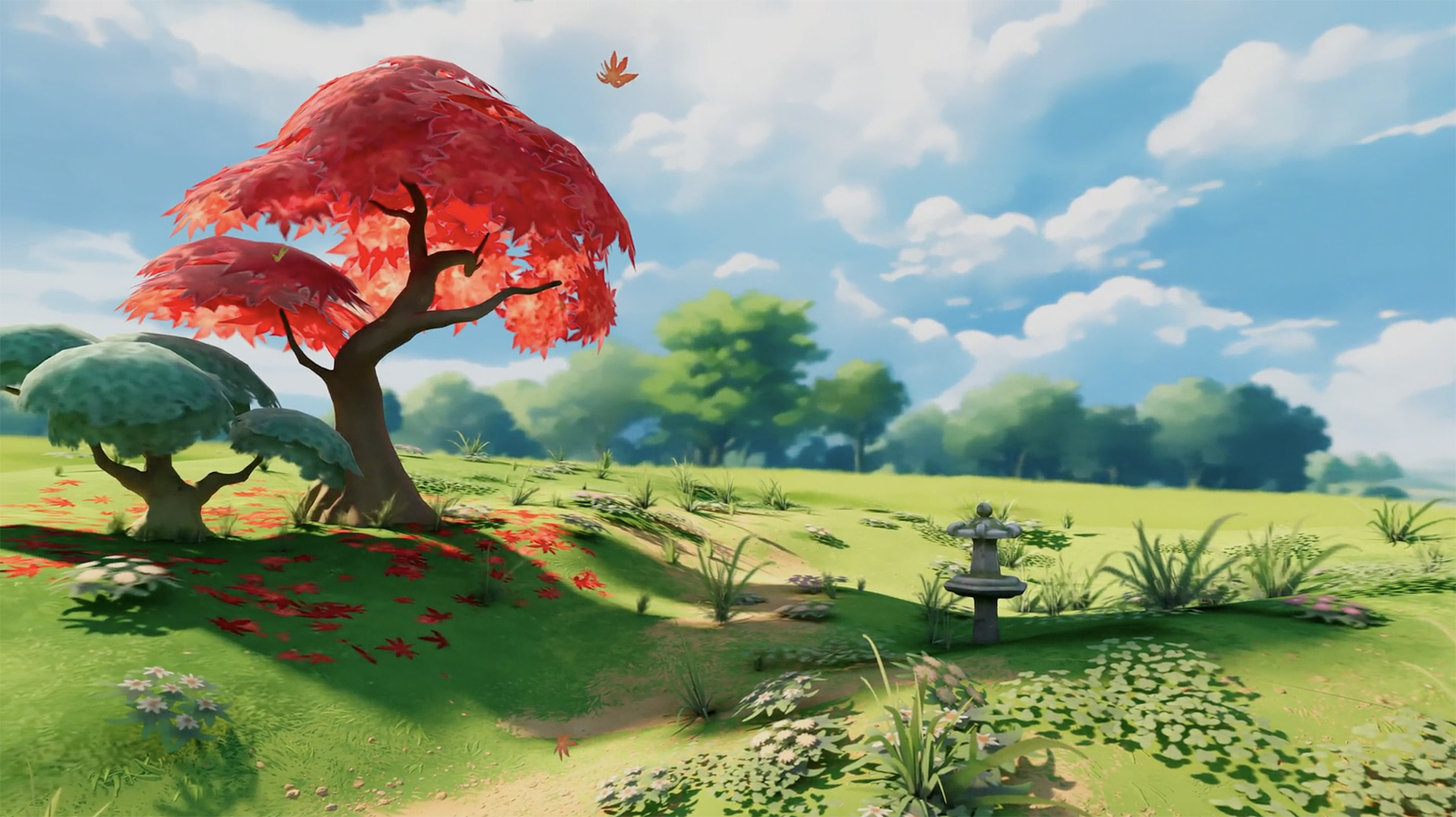

Safari for visionOS 2 supports the new WebXR transient-pointer input mode. It lets you make the most of natural input on visionOS, and allow your users to interact with a look and a pinch.
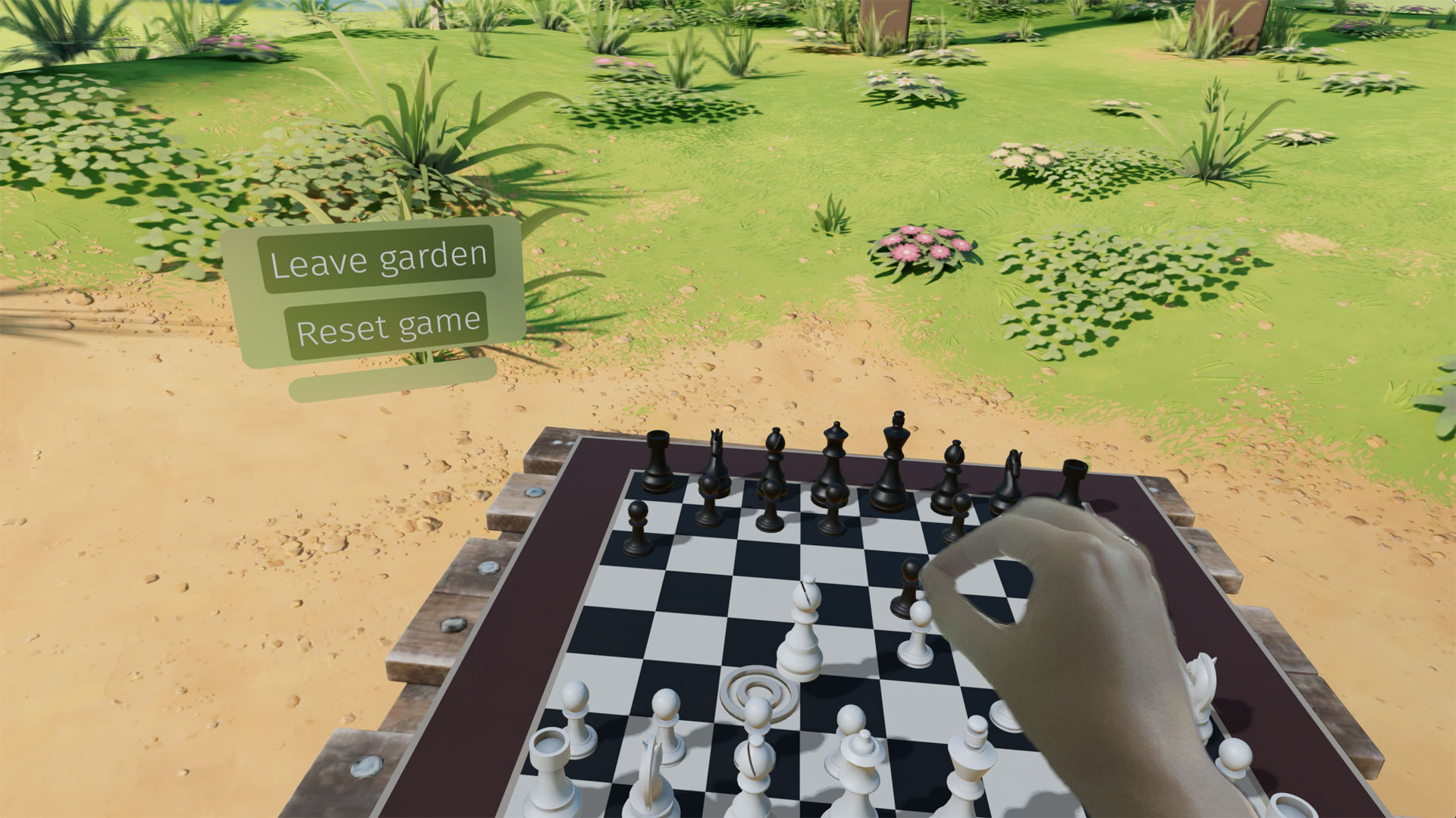

transient-pointer in your WebXR experience to support interactions like this, where players use their hands to pinch and drag as they move chess pieces around.If you want to animate a 3D model of the user’s hands, Safari for visionOS 2 also includes support for WebXR hand tracking. To ensure privacy, permission to allow hand tracking will be requested from users at the start of their WebXR session.
Learn all about WebXR on visionOS 2 by watching Build immersive web experiences with WebXR from WWDC. Learn more about transient-pointer input mode by reading Introducing natural input for WebXR in Apple Vision Pro. And learn all about how to use Safari’s developer tools on Mac to inspect and debug in Apple Vision Pro by reading Try out your website in the spatial web.
Spatial photos and panoramas
One of the amazing experiences you can have on Apple Vision Pro is looking at spatial photos and panoramas. The web is a great place to share these photos with others.
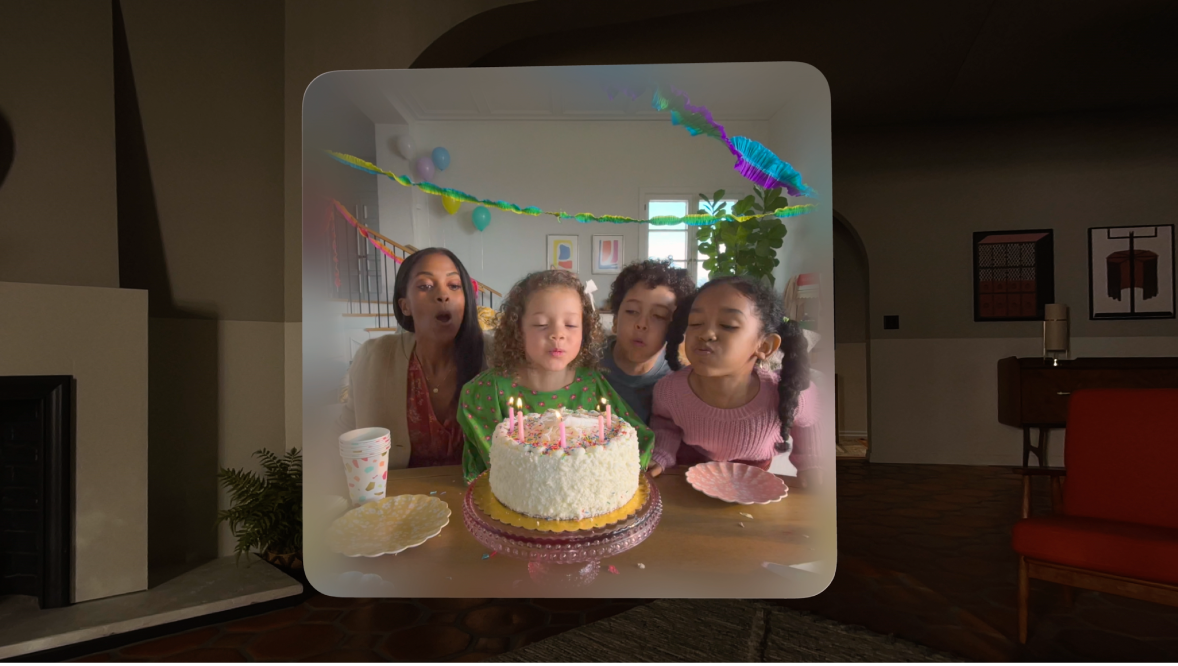

When you open the Photos app in visionOS, you see your library of photos. When you tap an image, it appears alone in a floating frame in front of you. Spatial photos appear at just the right height and viewing angle to make it feel like you’ve gone back to a moment in time. A second tap of the UI breaks a spatial photo out of its frame, becoming even more immersive. Similarly, a panorama floats in a frame on first tap. Then on second tap of the UI, it expands to wrap all around you, creating a fully immersive experience.
Now in Safari 18.0 for visionOS 2, you can use the JavaScript Fullscreen API to create a similar experience on the web. You can embed the photo in a web page, and provide the ability to tap. The photo will pop into a floating frame as the Safari window disappears. Then when the user taps on the spatial photo or panorama UI that visionOS provides, the photo will further expand to create a more immersive experience. When they exit the image, the Safari window will return.
Let’s walk through how to support experiencing a spatial photo or panorama on the web using Fullscreen API. First, include the image on your web page using any of the techniques used for years. Here, we can embed a flattened panoramic photo into the web page using simple HTML.
<img src="panorama.jpeg" class="go-fullscreen" alt="[description]">
Then using JavaScript, we’ll trigger .requestFullscreen() on tap. Perhaps like this.
document.querySelectorAll('.go-fullscreen').forEach(element => {
element.addEventListener('click', async () => {
await element.requestFullscreen();
});
});
You could, of course, create your own UI for the user to tap, rather than making the entire photo the tap target.
Spatial images work just the same, although it’s likely we want to provide fallbacks for browsers that do not support HEIC files. We can do so with the picture element.
<picture>
<source srcset="spatial.heic" type="image/heic">
<source srcset="fallback.avif" type="image/avif">
<img src="fallback.jpg" class="go-fullscreen" alt="write descriptive text here" >
</picture>
Spatial images are stereoscopic, with both a left and right channel. In Safari, when the image is embedded in the web page, the browser will show the left channel. And there’s no need to worry about providing a fallback of any sort for Safari on macOS, iOS, or iPadOS — the stereoscopic HEIC file works great.
This technique will also cause images to go fullscreen in any browser that supports Fullscreen API. Learn more about adding panorama and spatial photos to your websites by watching Optimize for the spatial web from WWDC.
Shaping interaction regions on visionOS
As a web developer, you’re very familiar with how link styling works on the web. For decades you’ve been able to use CSS to style text-decoration, color and more for :link, :hover, :active, and :visited states. You’ve also been able to adjust the size of the invisible tap target through use of padding.
Apple Vision Pro adds a new dimension to how links work — tap targets are visible on visionOS. Anytime a user looks at an interactive element, it’s highlighted to let them know that it can be tapped. And you as a designer or developer can intentionally design how an interaction region looks. You may want to add padding, for instance, or even a rounded corner to the otherwise invisible box.
Now in Safari in visionOS 2 , when you use CSS clip-path to change the shape of tappable area of a link, the visible interaction region will change shape as well. Interactive UI elements built with SVG and cursor: pointer will also be highlighted with the proper shape. Learn more by watching Optimize for the spatial web from WWDC.
Video on visionOS
Safari for visionOS 2 adds support for docking fullscreen videos into the current Environment. Anytime a user is watching a video fullscreen, they can tap the mountain symbol to enter an immersive experience. Turning the Digital Crown adjusts the immersion.
HTML
Writing Suggestions
At last year’s WWDC, Apple unveiled inline predictive text on iOS, iPadOS, macOS and more. It helps users input text faster by predicting what they might be typing and finishing the word, phrase or even a whole sentence when the user taps the space bar. Now, WebKit for Safari 18.0 on iOS, iPadOS, visionOS, macOS Sequoia and macOS Sonoma brings inline predictive text to the web.
While inline predictive text makes for a fantastic, personalized user experience, there might be specific situations on the web where it’s better to not have predictions. WebKit for Safari 18.0 on iOS, iPadOS, visionOS, macOS Sequoia and macOS Sonoma gives web developers the opportunity to disable inline predictions through the writingsuggestions attribute. By default, writing suggestions is set to true. You can turn off the capability by including the writingsuggestions="false" attribute on any type of text input field.
writingsuggestions.
Switch
WebKit for Safari on iOS 18 adds haptic feedback for <input type=checkbox switch>. This means, now when a user taps a switch control on iPhone, a single tap is felt — just like how toggling a switch feels in Settings app on iOS. Try this demo to see what it’s like.
Date and time inputs
WebKit for Safari 18.0 on macOS improves accessibility support for date and time input field types. Now <input type="date">, <input type="datetime-local">, and <input type="time"> elements work properly with VoiceOver.
ARIA
Usually elements have the labels they need, but sometimes there is no text label for a particular button or UI. In this situation, ARIA can be used to provide an accessible label. The aria-label attribute provides names of labels while aria-roledescription provides the description for the role of an element.
On very rare occasions, you may need to override aria-label or aria-roledescription to provide different names or descriptions specifically for braille. The aria-braillelabel and aria-brailleroledescription attributes provide such an ability. They exist to solve very specific needs, including educational contexts where the site needs to render the specific braille table dot pattern. If you do use braille-related ARIA attributes, be sure to test them using a braille reader. If in doubt, relying on the accessible name from content or aria-label / aria-roledescription is almost always the better user experience. WebKit has supported these ARIA attributes for years.
Now, WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for the ariaBrailleLabel and ariaBrailleRoleDescription element reflection properties. These make it possible to get and set the aria-braillelabel and aria-brailleroledescription ARIA attributes on DOM elements directly via JavaScript APIs, rather than by using setAttribute and getAttribute.
JavaScript
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for Unicode 15.1.0 characters in RegExp. Unicode 15.1 added 627 characters, bringing the total of characters to 149,813. Now, these new characters can be used in regular expressions.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 also adds support for the v flag with RegExp.prototype[Symbol.matchAll]. providing more powerful ways to match Unicode characters, as specified in the ECMAScript 2024 standard.
For example, you can now specify to only match on Latin characters, while avoiding matching on Cyrillic script characters.
const regex = /\p{sc=Latin}/v;
console.log(regex.test('A')); // true, 'A' is a Latin script character
console.log(regex.test('А')); // false, 'А' is a Cyrillic script character
Or split a string matching on Emojis.
"a 🥰 b 🥰".split(/[\p{Emoji}--\p{ASCII}]/v)// ["a ", " b ", ""]
Web API
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for URL.parse(), a way to parse URLs which returns null rather than an exception when parsing fails.
// Before
let url = null;
try {
url = new URL(input, base);
} catch(e) { }
// Now
const url = URL.parse(input, base);
WebKit for Safari 18.0 expands Declarative Shadow tree support by adding the shadowRootDelegatesFocus and shadowRootClonable IDL attributes to the <template> element. It also adds the shadowRootSerializable attribute and shadowRootSerializable IDL attribute to the <template> element, enabling those using Declarative Shadow roots to opt into making them serializable. Serializing can be done through the new getHTML() method that has been added at the same time.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for PopStateEvent’s hasUAVisualTransition, indicating whether the user agent has a visual transition in place for the fragment navigation.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for subresource integrity in imported module scripts, which gives cryptographic assurances about the integrity of contents of externally-hosted module scripts.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for the bytes() method to the Request, Response, Blob, and PushMessageData objects. This replaces the need for web developers to call arrayBuffer(), which can be difficult to use, and wraps the result in a Uint8Array . Calling bytes() is now the recommended way going forward when you need to access the underlying bytes of the data these objects represent.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for feature detecting text fragments by exposing document.fragmentDirective. Note that the returned object (a FragmentDirective) doesn’t provide any functionality, but it’s helpful if you need to know if Fragment Directives are supported by the browser.
Canvas
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for the willReadFrequently context attribute for the getContext() method. It indicates whether or not a lot of read-back operations are planned. It forces the use of a software accelerated 2D or offscreen canvas, instead of hardware accelerated. This can improve performance when calling getImageData() frequently.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 extends 2D canvas support for currentcolor. It can now be used inside color-mix() or Relative Color Syntax. Here currentcolor will default to the computed color property value on the canvas element.
Managed Media Source
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds Workers support for both Managed Media Source (MMS) and Media Source Extensions (MSE). This can be especially helpful on complex websites that want to ensure continuous and smooth video playback even when other site activity (such as live commenting) causes a very busy main thread. You can see the performance difference in this demo.
WebRTC
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for the WebRTC HEVC RFC 7789 RTP Payload Format. Previously, the WebRTC HEVC used generic packetization instead of RFC 7789 packetization. This payload format provides a new option for improving videoconferencing, video streaming, and delivering high-bitrate movies and TV shows.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for MediaStreamTrack processing in a dedicated worker. And it adds support for missing WebRTC stats.
HTTPS
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for secure HTTPS for all images, video, and audio by upgrading passive subresource requests in mixed content settings. This means that if some files for a website are served using HTTPS and some are served using HTTP (known as “mixed content”), all images and media will now be auto-upgraded to HTTPS, in adherence with Mixed Content Level 2.
WebGL
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for six new WebGL extensions:
EXT_texture_mirror_clamp_to_edgeWEBGL_render_shared_exponentWEBGL_stencil_texturingEXT_render_snormOES_sample_variablesOES_shader_multisample_interpolation
Web Inspector
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for fuzzy search code completion in the Web Inspector’s CSS source editor.
Passkeys
Two years ago at WWDC22, we announced support for passkeys — a groundbreaking industry-standard way to login to websites and app services. Passkeys provide people with an extremely easy user experience, while delivering a profound increase in security. To learn more, watch Meet Passkeys or read Supporting passkeys.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for three new features as we continue to improve passkeys. First, Safari 18.0 adds support for using mediation=conditional for web authentication credential creation. This allows websites to automatically upgrade existing password-based accounts to use passkeys. Learn more by watching Streamline sign-in with passkey upgrades and credential managers from WWDC.
Second, WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for using passkeys across related origins. This lets websites use the same passkey across a limited number of domains which share a credential backend.
And third, WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for the WebAuthn prf extension. It allows for retrieving a symmetric key from a passkey to use for the encryption of user data.
Safari Extensions
Safari 18.0 also adds support for Mobile Device Management of extension enabled state, private browsing state, and website access on managed devices. This means schools and businesses that manage iOS, iPadOS, or macOS devices can now include the configuration of Safari App Extensions, Content Blockers, and Web Extensions in their management.
Apple Pay
WebKit for Safari 18.0 adds support for funds transfer via Apple Pay.
Deprecations
While it’s rare to deprecate older technology from the web, there are occasions when it makes sense. We’ve been busy removing -webkit prefixed properties that were never standardized, aging media formats that were never supported in other browsers, and more. This helps align browser engines, improve interoperability, and prevent compatibility problems by reducing the possibility that a website depends on something that’s not a web standard.
Canvas
WebKit for Safari 18.0 removes support for OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D’s commit() method.
CSS
WebKit for Safari 18.0 deprecates support for a number of rarely used -webkit prefixed CSS pseudo-classes and properties — and even one -khtml prefixed property.
-webkit-altandaltproperties:-webkit-animating-full-screen-transitionpseudo-class:-webkit-full-screen-ancestorpseudo-class:-webkit-full-screen-controls-hiddenpseudo-class:-webkit-full-page-mediapseudo-class:-webkit-full-screen-documentpseudo-class:-khtml-dragpseudo-class
WebKit for Safari 18.0 also deprecates support for the resize: auto rule. Support for the resize property remains, just as it’s been since Safari 4. The values Safari continues to support include: none, both, horizontal, vertical, block, inline, plus the global values. Early versions of CSS Basic User Interface Module Level 3 defined auto, but it was later written out of the web standard.
WebKit for Safari 18.0 also deprecates support for non-standardize WEBKIT_KEYFRAMES_RULE and WEBKIT_KEYFRAME_RULE API in CSSRule.
Images
WebKit for Safari 18.0 removes support for the JPEG2000 image format. Safari was the only browser to ever provide support.
If you’ve been serving JPEG2000 files using best practices, then your site is using the picture element to offer multiple file format options to every browser. Safari 18.0 will simply no longer choose JPEG2000, and instead use a file compressed in JPEG XL, AVIF, WebP, HEIC, JPG/JPEG, PNG, or Gif — choosing the file that’s best for each user. Only one image will be downloaded when you use <picture>, and the browser does all the heavy lifting.
We have noticed that some Content Deliver Networks (CDN) use User Agent sniffing to provide one file to each UA, offering only JPEG2000 images to Safari — especially on iPhone and iPad. If you expect this might be happening with your site, we recommend testing in Safari 18.0 on both macOS Sequoia and iOS or iPadOS 18. If you see problems, contact your SaaS provider or change your image delivery settings to ensure your website provides fallback images using industry best practices.
If you notice a broken site, please file an issue at webcompat.com.
JavaScript
WebKit for Safari 18.0 removes [[VarNames]] from the global object to reflect changes in the web standard, a change that now allows this code to work:
<script>
eval('var x;')
</script>
<script>
let x;
</script>
Media
WebKit for Safari 18.0 removes support for non-standard VTTRegion.prototype.track.
Storage
WebKit for Safari 18.0 removes the last bits of support for AppCache.
When AppCache first appeared in 2009, in Safari 4, it held a lot of promise as a tool for caching web pages for use offline. It was imagined as “HTML5 Application Cache” back when HTML itself was being further expanded to handle more use cases for web applications. A developer could create a simple cache manifest file with a list of files to be cached. Its simplicity looked elegant, but there was no mechanism for cache busting, and that made both developing a site and evolving the site over time quite frustrating. AppCache also had security challenges. So new web standards were created to replace it. Today, developers use Service Workers and Cache Storage instead.
WebKit deprecated AppCache with a warning to the Console in Safari 11.0. Then in 2021, we removed support for AppCache from Safari 15.0, with a few exceptions for third-party users of WKWebView. Now we are removing those exceptions. This change to WebKit will only affect the rare web content loaded in older third-party apps that have JavaScript code which relies on the existence of AppCache related interfaces.
SVG
WebKit for Safari 18.0 removes the SVGAnimateColorElement interface, as well as the non-standard getTransformToElement from SVGGraphicsElement.
Web API
WebKit for Safari 18.0 removes support for four non-standard Web APIs:
KeyboardEvent.altGraphKey- AES-CFB support from WebCrypto
KeyboardEvent.prototype.keyLocationHashChangeEvent’s non-standardinitHashChangeEvent()method
WebView
Deprecated some legacy WebKit notification names including:
WebViewDidBeginEditingNotificationWebViewDidChangeNotificationWebViewDidEndEditingNotificationWebViewDidChangeTypingStyleNotificationWebViewDidChangeSelectionNotification
Bug Fixes and more
In addition to all the new features, WebKit for Safari 18.0 includes work to polish existing features.
Accessibility
- Fixed role assignment for
<header>inside<main>and sectioning elements. - Fixed range input not firing an input event when incremented or decremented via accessibility APIs.
- Fixed setting
aria-hiddenon a slot not hiding the slot’s assigned nodes. - Fixed VoiceOver to read hidden associated labels.
- Fixed comboboxes to expose their linked objects correctly.
- Fixed VoiceOver support for
aria-activedescendanton macOS. - Fixed time input accessibility by adding labels to subfields.
- Fixed
aria-hidden=trueto be ignored on the<body>and<html>elements. - Fixed
datetimevalues being exposed to assistive technologies in the wrong timezone. - Fixed wrong
datetimevalue being exposed to assistive technologies fordatetime-localinputs. - Fixed ignored CSS content property replacement text when it is an empty string.
- Fixed the computed role for these elements:
dd,details,dt,em,hgroup,option,s, andstrong. - Fixed hidden elements targeted by
aria-labelledbyto expose their entire subtree text, not just their direct child text. - Fixed accessible name computation for elements with
visibility: visibleinside a container withvisibility: hidden. - Fixed updating table accessibility text when its caption dynamically changes.
- Fixed updating
aria-describedbytext after the targeted element changes its subtree.
Animations
- Fixed the
transitionproperty to produce the shortest serialization. - Fixed the
animationproperty to produce the shortest serialization.
Apple Pay
- Fixed arbitrary 8 digit limit on a line item’s total amount.
Authentication
- Fixed
navigator.credentials.create()rejects with “NotAllowedError: Operation Failed” after a conditional UI request is aborted. - Fixed setting the cancel flag once the cancel completes regardless of a subsequent request occurring.
Canvas
- Fixed
drawImage(detachedOffscreenCanvas)to throw an exception. - Fixed OffscreenCanvas failing to render to the placeholder with nested workers.
- Fixed losing the contents layer of the placeholder canvas of OffscreenCanvas when switching off the tab.
- Fixed
drawImageto not alter the input source or the destination rectangles. - Fixed toggling the visibility on a canvas parent undoing the effect of
clearRect(). - Fixed the Canvas
drawImage()API to throw an exception when the image is in broken state. - Fixed a detached OffscreenCanvas to not transfer an ImageBuffer.
Cookies
- Fixed treating the lack of an explicit “SameSite” attribute as “SameSite=Lax”.
CSS
- Fixed setting
white-spaceto a non-default value dynamically on a whitespace or a new line. - Fixed custom counter styles
disclosure-openanddisclosure-closedto point to the correct direction in right-to-left. - Fixed
backface-visibilityto create a stacking context and containing block. - Fixed
getComputedStyle()to work with functional pseudo-elements like::highlight(). - Fixed: Aliased
:-webkit-full-screenpseudo-class to:fullscreen. - Fixed: Aliased
:-webkit-any-linkto:any-linkand:matches()to:is(). - Fixed
getComputedStyle()pseudo-element parsing to support the full range of CSS syntax. - Fixed
@supportsto correctly handle support for some-webkitprefixed pseudo-elements that were incorrectly treated as unsupported. - Fixed updating media-query sensitive meta tags after style changes.
- Fixed changing color scheme to update gradients with system colors or
light-dark(). - Fixed incorrect inline element size when using
font-variant-caps: all-small-capswithfont-synthesis. - Fixed
:emptyselector to work with animations. - Fixed preserving whitespace when serializing custom properties.
- Fixed updating style correctly for non-inherited custom property mutations.
- Fixed element removed by parent to end up losing the last remembered size.
- Fixed an incorrect difference between implicit and explicit initial values for custom properties.
- Fixed the contrast of Menu and MenuText system colors.
- Fixed keeping the shorthand value for CSS
gapas-is in serialized and computed values. - Fixed the style adjuster for
@starting-styleincorrectly invoking with a null element. - Fixed excluding
-apple-pay-buttonfrom applying to any element that supportsappearance: autoand is not a button. - Fixed missing color interpretation methods added to CSS color specifications.
- Fixed
hsl()andhsla()implementation to match the latest spec changes. - Fixed the implementation of
rgb()andrgba()to match the latest spec. - Fixed the
hwb()implementation to match the latest spec. - Fixed the remaining color types to be synced with the latest spec changes.
- Fixed carrying analogous components forward when interpolating colors.
- Fixed applying the fill layer pattern for
mask-mode. - Fixed
backdrop-filter: blurto render for elements not present when the page is loaded. - Fixed: Improved large Grid performance.
- Fixed some CSS properties causing quotes to be reset.
Editing
- Fixed an issue where input method editing would sporadically drop the composition range.
- Fixed dictation UI no longer showing up when beginning dictation after focusing an empty text field. (FB14277296)
Forms
- Fixed displayed
datalistdropdown to sync itsoptionselements after a DOM update. - Fixed input elements to use the
[value]as the first fallback step base. - Fixed
<select multiple>scrollbars to match the used color scheme. - Fixed updating the input value when selecting an
<option>from a<datalist>element. (FB13688998) - Fixed the value attribute not getting displayed in an
inputelement withtype="email"and themultipleattribute. - Fixed the iOS animation for
<input type=checkbox switch>. - Fixed form controls drawing with an active appearance when the window is inactive.
- Fixed constructed FormData object to not include entries for the image button submitter by default.
History
- Fixed the properties of
Historyto throw a SecurityError when not in a fully active Document.
HTML
- Fixed “about:blank”
document.referrerinitialization. - Fixed parsing a self-closing SVG script element. It now successfully executes.
JavaScript
- Fixed
RegExp.prototype.@@splitto update the following legacy RegExp static properties:RegExp.input,RegExp.lastMatch,RegExp.lastParen,RegExp.leftContext,RegExp.rightContext, andRegExp.$1, ... RegExp.$9. - Fixed
String.prototype.replaceto not take the fast path if the pattern is RegExp Object and thelastIndexis not numeric. - Fixed spec compliance for Async / Await, Generators, Async Functions, and Async Generators.
- Fixed async functions and generators to properly handle promises with throwing “constructor” getter.
- Fixed
returnin async generators to correctlyawaitits value. - Fixed
Symbol.speciesgetters to not share a single JS Function. - Fixed throwing a
RangeErrorifSetmethods are called on an object with negativesizeproperty. - Fixed
eval()function from another realm to not cause a directevalcall. - Fixed
eval()call with...spreadsyntaxt to be a direct call. - Fixed try/catch to not intercept errors originated in
[[Construct]]of derived class. - Fixed several issues:
- direct
eval()in a default value expression inside a rest parameter creates a variable in the environment of the function rather than the separate one of the parameters; - a ReferenceError is thrown when accessing a binding, which is defined inside rest parameter, in
eval(), or a closure created in a default value expression of a preceding parameter, but only if there is avarbinding by the same name; - a closure, created in the default value expression inside a rest parameter, is created in a different VariableEnvironment of the function than its counterparts in preceding parameters which causes the incorrect environment to be consulted when querying or modifying parameter names that are “shadowed” by
varbindings.
- direct
- Fixed TypedArray sorting methods to have a special-case for camparator returning
false. - Fixed programming style for bitwise and in setExpectionPorts.
- Fixed
emitReturn()to loadthisvalue from arrow function lexical environment prior to the TDZ check. - Fixed NFKC normalization to work with Latin-1 characters.
- Fixed parsing of private names with Unicode start characters.
- Fixed
instanceofto not get RHS prototype when LHS is primitive. - Fixed bracket update expression to resolve property key at most once.
- Fixed bracket compound assignement to resolve the property key at most once.
- Fixed
Object.groupByandMap.groupByto work for non-objects. - Fixed
Array.fromAsyncto not call the Array constructor twice. - Fixed inconsistent output of
Function.prototype.toStringfor accessor properties. - Fixed
Set#symmetricDifferenceto callthis.hasin each iteration. - Fixed logical assignment expressions to throw a syntax error when the left side of the assignment is a function call.
- Fixed throwing a syntax error for nested duplicate-named capturing groups in RegEx.
- Fixed
ArrayBufferandSharedArrayBufferconstructor to check length before creating an instance. - Fixed Intl implementation to ensure canonicalizing “GMT” to “UTC” based on a spec update.
- Fixed RegEx lookbehinds differing from v8.
- Fixed
fractionalDigitsofIntl.DurationFormatto be treated as at most 9 digits if it is omitted. - Fixed optimized TypedArrays giving incorrect results.
- Fixed
Intl.DurationFormatfornumericand2-digit.
Loading
- Fixed
navigator.cookieEnabledto returnfalsewhen cookies are blocked.
Media
- Fixed MediaSession to determine the best size artwork to use when the
sizesmetadata attribute is provided. (FB9409169) - Fixed video sound coming from another window after changing tabs in the Tab Bar in visionOS.
- Fixed playback for MSE videos on some sites.
- Fixed allowing a video’s
currentTimeto be further than the gap’s start time. - Fixed broken audio playback for a WebM file with a Vorbis track.
- Fixed
sampleRateandnumberOfChannelsto be required and non-zero in a valid AudioEncoderConfig. - Fixed media elements appending the same media segment twice.
- Fixed an issue where Safari audio may be emitted from the wrong window in visionOS.
- Fixedrejecting valid NPT strings if ‘hours’ is defined using 1 digit.
- Fixed picture-in-picture when hiding the
<video>element while in Viewer. - Fixed the return button not working after the video is paused and played in picture-in-picture.
Networking
- Fixed upgrading inactive or passive subresource requests and fetches in would-be mixed security contexts to match standards.
- Fixed incorrect
Sec-Fetch-Sitevalue for navigation of a nested document. - Fixed loading WebArchives with a non-persistent datastore.
- Fixed
Timing-Allow-Originto not apply to an HTTP 302 response.
- Fixed print buttons with a print action implementation.
- Fixed Open in Preview for a PDF with a space in its name.
- Fixed “Open with Preview” context menu item to work with locked PDF documents.
Rendering
- Fixed Greek uppercase transforms failing for some characters.
- Fixed resizing a
<textarea>element with1rempadding. - Fixed the color correctness of the color matrix filter.
- Fixed
backdrop-filterto apply to the border area of an element with aborder-radius. - Fixed intrinsic inline size calculators to account for whitespace before an empty child with nonzero margins.
- Fixed overlapping elements with flex box when
height: 100%is applied on nested content. - Fixed incorrect grid item positioning with out-of-flow sibling.
- Fixed
break-wordwith a float discarding text. - Fixed
min-contentcalculation for unstyledonly-childinlines elements. - Fixed ellipsis rendering multiple times when
position: relativeandtopare used. - Fixed a bug for inline elements inserted in reverse order after a block in a continuation.
- Fixed the flash of a page background-colored bar in the footer when the window is resized.
- Fixed garbled bold text caused by glyph lookup using the wrong font’s glyph IDs when multiple installed fonts have the same name. (FB13909556)
- Fixed selecting Japanese text annotated with
rubyin avertical-rlwriting mode table. - Fixed support for border, padding, and margin on
mfracandmspaceelements in MathML.
Scrolling
- Fixed the cursor not updating as content scrolls under it on some pages.
Security
- Fixed stripping the scroll-to-text fragment from the URL to prevent exposing the fragment to the page.
- Fixed CORS bypass on private localhost domain using 0.0.0.0 host and mode “no-cors”.
- Fixed blocking cross-origin redirect downloads in an iframe.
- Fixed blocked cross-origin redirect downloads to attempt rendering the page instead.
SVG
- Fixed the SVG parser to interpret “form feed” as white space.
- Fixed error handling for invalid filter primitive references.
- Fixed displaying an SVG element inside a
<switch>element. - Fixed SVG title to have
display: noneas the default UA style rule. - Fixed the UA stylesheet for links in SVGs to apply
cursor: pointermatching standards. - Fixed returning the initial value for the SVG gradient
stop-colorif it is not rendered in the page. - Fixed the SVG marker segment calculations if the marker path consists of sub-paths.
- Fixed
SVGLengthto sync with the WebIDL specification.
Text
- Fixed disclosure counter styles to consider
writing-mode.
Web Animations
- Fixed percentage transform animations when
widthandheightare animated. - Fixed updating an animation when changing the value of a
transformproperty while that property is animated with an implicit keyframe. - Fixed
displaytransition tonone.
Web API
- Fixed
cssTextsetter to change thestyleattribute when the serialization differs. (FB5535475) - Fixed
history.pushState()andhistory.replaceState()to ignore thetitleargument. - Fixed URL text fragment directives not fully stripped from JavaScript.
- Fixed
showPicker()method to trigger suggestions from adatalist. - Fixed
langattribute in no namespace to only apply to HTML and SVG elements. - Fixed unnecessarily unsetting the iframe fullscreen flag.
- Fixed DOM Range to correctly account for CDATASection nodes.
- Fixed
getGamepads()to no longer trigger an insecure contexts warning. - Fixed inserting a
<picture>element displaying the same image twice. - Fixed throwing exceptions in navigation methods if in a detached state.
- Fixed a minor issue in URL’s host setter.
- Fixed cloning of ShadowRoot nodes following a DOM Standard clarification.
- Fixed GeolocationCoordinates to expose a
toJSON()method. - Fixed IntersectionObserver notifications that sometimes fail to fire.
- Fixed GeolocationPosition to expose a
toJSON()method. - Fixed setting
CustomEvent.targetwhen dispatching an event. - Fixed
navigator.languageonly returning the system language in iOS 17.4. - Fixed: Removed presentational hints from the
widthattribute for<hr>. - Fixed an issue when inserting writing suggestions into an editable
display: gridcontainer. - Fixed the warning message for
window.styleMedia.
Web Apps
- Fixed resolving
www.sub-domain for Associated Domains for all web apps.
Web Assembly
- Fixed initialization of portable reference typed globals.
Web Extensions
- Fixed getting an empty key from storage. (FB11427769)
- Fixed Service Workers not appearing in the Develop menu or remote Web Inspector menu. (130712941)
- Fixed web extensions unable to start due to an issue parsing declarativeNetRequest rules. (FB14145801)
Web Inspector
- Fixed font sizes in the Audits tab.
- Fixed expanded sections of Storage to not collapse.
- Fixed Web Inspector to show nested workers.
- Fixed CSS font property values marked
!importantnot getting overridden when using the interactive editing controls. - Fixed an issue where the Web Inspector viewport might appear cut off.
- Fixed runtimes to be aligned in the Audit tab.
- Fixed remembering the message type selection in the Console tab.
- Fixed autocomplete for the
text-indentproperty suggesting prefixed properties instead ofeach-lineorhanging. - Fixed
backgroundautocompletion suggestion to includerepeating-conic-gradient. - Fixed the list of breakpoints in the Sources tab disappearing when Web Inspector is reloaded.
- Fixed console clearing unexpectedly when Web Inspector reopens.
- Fixed console code completion to be case-insensitive.
- Fixed
overflow: scrollelements to scroll as expected when highlighting an element from the DOM tree. - Fixed showing additional Safari tabs from an iOS device in the Develop menu.
- Fixed Console and code editor completion not auto-scrolling the suggestion into view.
- Fixed search in the DOM tree view unexpectedly chaning the text display.
- Fixed clicking the “goto” arrow for computed CSS when “show independent Styles sidebar” is disabled.
- Fixed inspectable tabs from Safari in the visionOS Simulator don’t appear in Developer menu on the host macOS.
- Fixed Accessibility inspector for switch controls to report “State: on/off” instead of “Checked: true/false”.
Web Views
- Fixed Gamepad API in WKWebView.
- Fixed repainting HTML elements when their width or height change in legacy WebView.
WebDriver
- Fixed retrieving titles containing multibyte characters.
WebRTC
- Fixed RTCEncodedVideoFrame and RTCEncodedAudioFrame to match the WebIDL specification.
- Fixed VideoTrackGenerator writer to close when its generator track (and all its clones) are stopped.
- Fixed WebRTC AV1 HW decoding on iPhone 15 Pro.
- Fixed black stripes with screen sharing windows.
- Fixed black stripes with getDisplayMedia captured windows when the window is resized.
Updating to Safari 18.0
Safari 18.0 is available on iOS 18, iPadOS 18, macOS Sequoia, macOS Sonoma, macOS Ventura, and in visionOS 2.
If you are running macOS Sonoma or macOS Ventura, you can update Safari by itself, without updating macOS. Go to > System Settings > General > Software Update and click “More info…” under Updates Available.
To get the latest version of Safari on iPhone, iPad or Apple Vision Pro, go to Settings > General > Software Update, and tap to update.
Feedback
We love hearing from you. To share your thoughts on Safari 18.0, find us on Mastodon at @jensimmons@front-end.social and @jondavis@mastodon.social. Or send a reply on X to @webkit. You can also follow WebKit on LinkedIn. If you run into any issues, we welcome your feedback on Safari UI (learn more about filing Feedback), or your WebKit bug report about web technologies or Web Inspector. If you notice a website that seems broken in Safari, but not in other browsers, please file a report at webcompat.com. Filing issues really does make a difference.
Download the latest Safari Technology Preview on macOS to stay at the forefront of the web platform and to use the latest Web Inspector features.
You can also find this information in the Safari 18.0 release notes.
1. iPhone Mirroring is available on Mac computers with Apple silicon and Intel-based Mac computers with a T2 Security Chip. Requires that your iPhone and Mac are signed in with the same Apple ID using two-factor authentication, your iPhone and Mac are near each other and have Bluetooth and Wi-Fi turned on, and your Mac is not using AirPlay or Sidecar. iPhone Mirroring is not available in all regions.